Artificial Intelligence in Automobile Industry: AI Use Case in Self-Driving Cars

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the automobile industry rapidly; it has become an essential component of the auto-drive technology. The enormous amount of data collected through connected devices and services is the main enabling factor in the success of AI applications in any industry. Using AI, a human touch is added to computer applications and machines. A humungous amount of data is fed to these programs that are processed to think logically and perform human actions. While the industry is continuously striving towards fully autonomous (self-driving) cars, many companies are already offering advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
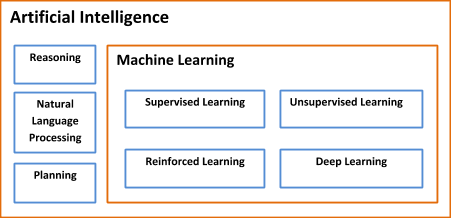
Are Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning the same?
AI is more like the umbrella concept of which Machine Learning (ML) is an integral part. The following diagram depicts the relationship:
Levels of Autonomy in Self-Driving Cars
When you think of autonomous cars, the first thought that comes to your mind is a car without a human driver. Well, it might come as a surprise that there are degrees to which a car is autonomous. The International Authority of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of autonomy for self-driving cars.
- Level 0 – No Automation
There is zero automation at this level. Majority of the vehicles on road today is manually controlled. There may be systems in place to help the driver, such as the emergency braking system but it doesn’t technically “drive” the car and so doesn’t qualify as automation.
- Level 1 – Driver Assistance
These vehicles provide only one automated system for driver assistance, such as adaptive cruise control. The human driver controls the steering and braking with adaptive cruise control, so it qualifies as Level 1 autonomy.
- Level 2 – Partial Driving Automation
This means the vehicle can control both steering and accelerating/decelerating. The human driver can take control of the car at any time.
- Level 3 – Conditional Automation
This is where environmental detection capabilities come into play. The car can make informed decisions, such as overtaking past a slow moving vehicle. However, the driver can override the control of the vehicle if the system is unable to execute a task.
- Level 4 – High Automation
These cars are fully automated for most circumstances. However, a human driver can manually override the system.
- Level 5 – Full Automation
These cars do not require a human driver and don’t even have steering wheels or acceleration/braking pedals.
Get To Know Other Data Science Students
Mikiko Bazeley
ML Engineer at MailChimp
Jonathan King
Sr. Healthcare Analyst at IBM
Peter Liu
Business Intelligence Analyst at Indeed
AI use case: How does Artificial Intelligence work in self-driving cars?
To better understand the role of AI in self-driving cars, let’s first take a look at the human perspective. A human driver uses sensory functions, such as vision and sound to watch the road, road signs, and other vehicles. The years of experience in driving helps the driver develop a habit to look for little things encountered on the roads – it could be a big bump or a pedestrian crossing.
The goal of the automotive industry is to build Level 5 autonomous cars that can drive like experienced human drivers. This means the vehicles need to have sensory functions, cognitive functions and executing capabilities. The process used to achieve this can be divided into three parts.
Part 1: Collection of data from the vehicles
Multiple sensors, cameras, and communication systems are fitted on the autonomous vehicles to generate data of the surrounding environment. This system collects information about everything the autonomous vehicle sees and hears on the road, such as other vehicles, the speed at which every vehicle around it is travelling, road infrastructure, and every object on/near the road. This data is then processed and used to communicate meaningful information (input) to the AI programs.
Part 2: AI Mastermind
The AI programs are stored in the cloud. When the cloud receives the processed data, it starts applying AI algorithms to add meaning to this enormous amount of data. The AI engine is the brain of this entire system and helps in making the right decisions. It is connected to a database that acts as a memory that stores previous driving experiences. These well-informed decisions are relayed to autonomous vehicles.
Part 3: Executing the AI Capabilities
Based on the decisions made by the AI engine, the autonomous vehicle knows what to do when it encounters a situation on road and hence it drives through traffic without any human intervention and reaches the destination safely.
For further reading, check out the data scientist job description here and learn more about data science.
Automation in automobile industry beyond driving
The automobile industry is not only focused on building autonomous vehicles; they want users to have a fully customized experience. To achieve this, autonomous vehicles are equipped with AI-based voice and speech recognition, gesture controls, eye tracking, and other driving monitoring systems to name a few. These functions also follow the same process as explained in the previous sections.
The driving experiences generated from each ride is recorded and stored in the database to help the AI programs make more accurate decisions in the future.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning is described as the fourth industrial revolution. It is transforming our lives and jobs and will continue to do so at a rapid pace for the next few years. About 20 years ago, AI was a farfetched though for the common man, something you watched only in science fiction movies. Now, AI is part of our daily lives, our smartphones, Google virtual assistant, and ride-sharing apps like Uber are just the tip of the iceberg. Going by current research and AI use cases, we can surely expect many advancements in the automobile industry in the coming years.Web development, Finance and Healthcare are few of the sectors where AI/Machine Learning is being widely adapted.
Since you’re here…Are you a future data scientist? Investigate with our free guide to what a data scientist actually does. When you’re ready to build a CV that will make hiring managers melt, join our Data Science Bootcamp that guarantees a job or your tuition back!



![87 Data Science Interview Questions [2022 Prep Guide]](https://www.springboard.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/87-data-science-interview-questions-2022-prep-guide-380x235.png)