How To Become a Data Scientist in 2023: 9-Step Guide

In this article

According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, being a data scientist is one of the top 10 fastest growing occupations in the U.S., with a projected growth of 31.4% by 2030. Coupled with a median salary of $131,490, it’s never been a better time to get into the field of data science.
But changing careers is not something that can be done overnight. From education and portfolio building to networking and interviewing, there are several steps budding data scientists must take before they are ready for their first day on the job.
While it can’t be denied that there’s a lot of work to be done, it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With our 9-step guide, you’ll be able to plan out and visualize clear goals that will help you progress toward your first role within the data science field. Keep reading if you’re ready to start working on landing your dream job!
What Is a Data Scientist?

Source: Tibco
A data scientist is a technology professional that works in the field of data gathering, wrangling, manipulation, and analysis. Often with backgrounds in computer science, mathematics, statistics, and business, data scientists in all their forms aim to understand the data they work with and then use it to illustrate or predict useful and profitable insights.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?
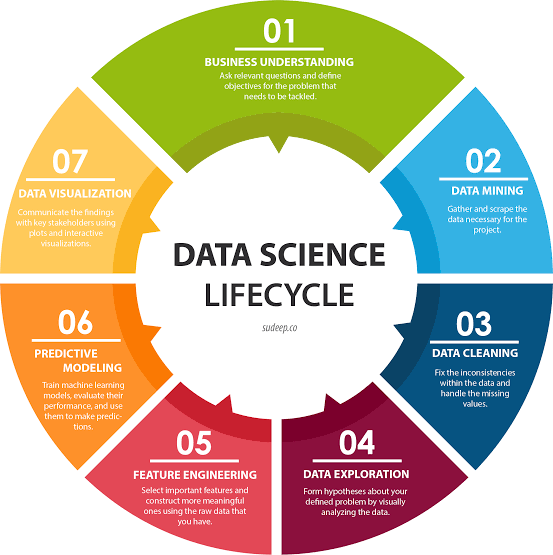
Source: Data Science Central
As data scientists often work with extremely large sets of data—or “big data” as it is sometimes referred to—a large amount of their time goes to gathering and readying data so that it can be used for various purposes.
Depending on the specifics of the role, a data scientist might then analyze this data to glean actionable business insights, feed it to an AI or machine learning project, design and write new software to streamline the data wrangling process, or store and organize it in a database.
Popular Roles Within Data Science
Here is a breakdown of some of the most popular roles and titles within the field of data science.
Data Scientist
A general role whose responsibilities may include:
- Gathering and wrangling large sets of data
- Designing software and algorithms to automate the data wrangling process
- Analyzing data through EDA (exploratory data analysis)
- Visualizing data so that the gained insights can be easily comprehended by various individuals
Data Engineer

A role that focuses on the collection and cleaning of data, with responsibilities such as:
- Creating systems and pipelines for efficient collection of data
- Organizing and structuring large sets of data for analysis
- Making the data produced by a company accessible and ready to be used by other data science roles
Note that this role is most often found at large companies where it is possible and efficient to have separate roles for wrangling data and for analyzing data. At smaller companies, both of these tasks may be delegated to a data scientist or data analyst.
Data Analyst
A role that is found in many industries such as tech, healthcare, entertainment, and finance.
Responsibilities include:
- Receiving questions and requests for information from stakeholders and decision-makers within a company
- Collecting relevant data and structuring it into relational databases ready for querying and analysis
- Gleaning actionable and profitable insights from the data and visualizing it for easy comprehension
- Presenting the findings and results to relevant employees within the company
Machine Learning Engineer
A specialist role involved with deep learning and artificial intelligence (AI).
Typical responsibilities include:
- Researching, designing, and building AI software that can adapt and develop its own practices as it receives new data
- Using AI and machine learning to automate processes
- Using machine learning to design predictive models which can be used to gain business insights
Related Read: What Is Predictive Analytics?
Database Administrator

A role that can be found in just about all industries that produce and/or make use of data.
Common responsibilities include:
- Structuring raw data into relational databases so that it can be stored efficiently
- Managing new additions to various databases
- Improving accessibility for employees and users
- Designing and implementing security features to keep data secure and stored according to law
Data Architect

A role is also found in many industries that are centered around the design and implementation of databases.
Responsibilities include:
- Designing large-scale data storage and structuring solutions for a company
- Deciding what kinds of databases should be made for what purposes
- Designing systems and pipelines for the collection and production of data
Business Analyst

A role found most prominently in the financial and retail sectors.
The responsibilities are as follows:
- Using data to pinpoint areas of potential improvement within a business
- Combining data analysis to find areas of inefficiency or wasteful practices, and business acumen to design solutions
- Using data visualization tools to present findings and convince decision makers to take action
Get To Know Other Data Science Students
Mengqin (Cassie) Gong
Data Scientist at Whatsapp
Isabel Van Zijl
Lead Data Analyst at Kinship
Garrick Chu
Contract Data Engineer at Meta
9 Steps to Becoming a Data Scientist
Here’s how you actually become a data scientist:
-
Brush Up on Data Science Fundamentals
-
Meet the Educational Requirements
-
Plan Your Career Path and Specialization
-
Hone Essential Skills
-
Familiarize Yourself With the Essential Data Science Tools
-
Gain Practical Experience by Working on Projects and Building Your Portfolio
-
Build Your Network
-
Pursue a Data Science Internship
-
Prepare for and Ace the Data Science Interview
1. Brush Up on Data Science Fundamentals

Niches and specialties cannot be worked on until the fundamentals of the trade have been perfected, so starting simple is never a waste of time! Here’s where you should focus your energy:
Statistical Analysis

This refers to analyzing data and presenting the findings through unbiased and accurate statistics.
Programming
Writing code and building software are key skills used in many areas of data science.
Data Visualization

Presenting data in tables, graphs, charts, and dashboards so that it can be quickly and easily comprehended by both technical and non-technical individuals.
Machine Learning

Creating software that “learns” from the data fed to it and uses it to spontaneously adapt its processes in response to unique situations.
2. Meet the Educational Requirements
Becoming a data scientist doesn’t require a college degree, but there are often some educational requirements you need to be mindful of before you attempt to land your first job.
You Don’t Need a Degree in Data Science, but a Bachelor’s Degree Can Be Helpful
Data science degrees are still relatively new college programs that combine elements of mathematics, computer science, statistics, and business science. As such, a separate degree or advanced degree in any of these or other relevant fields is a perfectly acceptable educational background for a data scientist.
Related Read: Data Science vs Statistics: Learn the Difference
Take a Certified Course or a Bootcamp
If you don’t have or don’t plan to get a college degree, there are other ways into the data science community. Taking a certified course or enrolling in a data science bootcamp is a great way to get an immersive, hands-on, and practical education in the fundamentals of not only the subject of data science but specifically the role of a data scientist itself.
3. Plan Your Career Path and Specialization
Once you have the fundamentals under control, beginning to plan a path for yourself and develop a niche or specialization is highly advantageous, and will give you an edge on the job market.
Related Read: 14 Data Science Careers to Consider [Skills, Salary, Role]
4. Hone Essential Skills
Earning certifications in data science or developing your own data science projects to showcase the following skills is a great way to demonstrate your ability.
Technical Skills

General technical skills are useful for IT professionals, as they work with computers every day and would save time and effort by knowing how to troubleshoot problems themselves.
- Programming Languages
It is expected for a data scientist to be fluent in Python, and generally familiar with another language or two, such as R or SQL.
- Data Mining
Data mining is the gathering of relevant and trustworthy data from different departments or areas of the company, and often from third parties as well.
- Data Visualization
Getting to grips with data visualization tools like Tableau, Microsoft Excel, and Google Charts to display data in a readable way is a key skill for data scientists.
- Data Analysis
This is the process of querying and analyzing structured data to find patterns and points of interest that can be translated into actionable insights and business opportunities.
- Statistics
Statistics provide unbiased insights based purely on numbers and data to help decision-makers separate fiction and feeling from fact when forming business plans.
- Machine Learning
Once you have studied the fundamental theoretics behind machine learning, you may want to pursue it as a specialization, which would mean furthering your study and working on your own machine learning projects.
- Deep Learning
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning that focuses on replicating human methods of learning certain kinds of information by designing artificial neural networks.
- Natural Language Processing
Another branch of machine learning, natural language processing (NLP) is used widely in the area of virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri or Amazon’s Alexa.
- Algorithms
Algorithms are sets of instructions that solve problems and perform computations. They can be trained to make automated decisions through the use of AI.
- Data Engineering
Data engineering skills refer to everything from gathering data to wrangling and cleaning it — basically all the steps that come before analysis.
Soft Skills

Data scientists need to communicate their findings to employees beyond the scope of their data science teams, which means explaining their results to people who do not have the same knowledge or skill set as they do. This requires soft skills in communication and presentation.
- Analytical Mindset
Data science isn’t just about finding the right answers from data sets, but also about forming the correct questions to ask, which requires an analytical mindset.
- Business Acumen
Many data scientists work with the goal of improving the company they work for, whether that means improving efficiency, raising profits, coming up with profitable ideas, or finding new ways to save money. As well as being able to read the data, data scientists need to understand what a business needs.
- Critical Thinking
Critical thinking helps root out anomalies and incorrect values with sets of data, and is therefore particularly useful during the data cleaning and wrangling process.
- Adaptability and Flexibility
Data is what it is, not what we want it to be, meaning it may not always show us the information we want. When hiccups occur, adaptability and flexibility are key to overcoming the problem and turning it into something useful.
- Collaboration And Teamwork
Data scientists usually work within a team and so need to work well together. They also need to collaborate with other departments to collect data and share their findings.
- Problem-Solving
Being a self-starter is a valuable trait for a data scientist. Working on solutions and improving your problem-solving skills will make you a great asset to any team.
- Communication
When a problem needs to be shared, a deadline extended, or a plan changed, swift and clear communication is key to maintaining a happy team and a healthy project.
- Patience And Persistence
Sifting through data can be a time-consuming process, and patterns will not always jump out willingly. Patience is key to finding those all-important actionable insights.
5. Familiarize Yourself With the Essential Data Science Tools
Here is a list of popular tools used within the field of data science so that you can get familiar with them.
Apache Spark

An analytics engine used for large-scale data engineering, processing, and machine learning.
Tableau
A data visualization tool that connects to databases and allows users to create powerful and varied visual representations of their data.
SAS
A statistical software suite designed to help users manage, analyze, predict, and visualize data.
MATLAB
A programming language used to develop algorithms and create models.
Python
Python is a programming language designed for readability and used frequently by 75% of data scientists.
R
A statistical programming language used by 47% of data scientists.
BigML
A popular machine learning platform.
6. Gain Practical Experience by Working on Projects and Building Your Portfolio
Developing a large, impressive, and high-effort portfolio is a great way to showcase your ability and passion, especially if you are lacking in formal education or experience. Creativity and individualism are highly valued, so no two portfolios need to be the same, and you can pick and choose from any and all data science projects that may interest you.
7. Build Your Network

Building your network is a good way to get your foot in the door when you’re first starting out in the field. It will help you develop your skills, make new friends with similar interests, work on your passion projects, and finally, find a job.
Linkedin is a useful tool if you use it correctly. Always connect with colleagues and acquaintances you make within the industry, even those that you simply attended an event with.
Online Communities
Online professional and amateur communities on platforms like Discord and Reddit are great places to exchange ideas.
Conferences and Meet-Ups
Becoming an active member of your local data science community doesn’t have to come after you’ve landed the job and made a name for yourself. Start attending conferences and meet-ups as soon and as often as you are able.
8. Pursue a Data Science Internship
If you are lucky enough that you can work for free or for limited pay, look into getting a data science internship to complement your study with real-life experience.
9. Prepare for and Ace the Data Science Interview
When preparing for a data science interview, research is key. Research the company, the people, the role, typical data science interview questions, and questions you should ask the interviewer.
How Much Can You Make as a Data Scientist?
Here are some average salaries for data scientists at different stages in their careers.
Entry-Level Data Scientist
For a data scientist’s first role, the average salary sits at around $110,179. However, even in your first data science or analysis role, salary negotiation is possible.
Related Read: 7 Entry-Level Data Science Jobs
Mid-Level Data Scientist
Mid-level data scientists will have around 2-4 years of experience and can expect to earn about $120,256.
Senior-Level Data Scientist
Senior-level professionals who are around 5-7 years into their data science career can expect to be offered around $150,910 annually. However, Glassdoor reports a top threshold of $307,000.
Where Can You Find Data Science Jobs?
Here are a few popular sites and communities where you’ll be able to find job postings and opportunities in the field of data science.
LinkedIn is a great way to form lasting connections with people you meet at community events and meetings.
Job Boards

Here are a few general and data-specific job boards to kickstart your job search. Checking these sites a few times a week is a great way to keep up to date on openings within the industry.
Network
Whether it’s getting to know the people in your office building, handing out business cards at events, or participating in online communities, every little bit of networking counts.
Slack Communities
While Slack is primarily used for internal communication within a company, its users have also made open Slack communities for discussion on specific topics. Data science communities like DataTalks.Club can be a place to learn and discuss data science, ask for career advice, and even network.
FAQs About Becoming a Data Scientist
Here are some FAQs about the path to becoming a data scientist.
Is It Hard To Become a Data Scientist?
It is not specifically easier or harder to become a data scientist compared to other jobs in the tech industry. If you are motivated and hard-working, you will be able to gain the skills needed to become a data scientist.
Can a Beginner Learn Data Science?
Yes, there are even data science bootcamps and online courses available that are catered specifically for beginners with no prior experience in the field.
Can You Become a Data Scientist Without a Degree?
Yes, there are other ways to showcase your data science skills and credentials, such as completing accredited online courses, earning official certifications, and developing an extensive portfolio.
Is Data Science a Stressful Job?
Data science is not reported to be a stressful job. In fact, Glassdoor reports that from a pool of 26,000 data scientists, the work/life balance for the job is rated at 4 out of 5 stars.
Since you’re here…
Thinking about a career in data science? Enroll in our Data Science Bootcamp, and we’ll get you hired in 6 months. If you’re just getting started, take a peek at our foundational Data Science Course, and don’t forget to peep our student reviews. The data’s on our side.