7 Incredible Ways AI Is Being Used in Space Exploration

In this article
For millennia, mankind has looked up at the night sky and been filled with a sense of wonder and curiosity. That same curiosity still burns brightly today. With the advancements of modern technology, humanity has been able to use artificial intelligence to explore the universe in ways never before imagined.
From robotics and satellite operations to data analysis, predictive maintenance, and galaxy mapping, artificial intelligence (AI) is helping us understand the mysteries of our universe and even explore it.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at seven incredible ways AI is being used in space exploration and what the future could look like.
Is AI Common in Space Exploration?
Yes! AI is currently being used in the space industry to help scientists analyze data more quickly and accurately and automate operations on spacecraft. The continuous development of AI is helping rovers and landers explore other planets and moons in ways never before possible. And all these combined contribute to new discoveries, making AI an invaluable tool that can help us learn more about the world beyond our own.
7 Ways AI Is Used in Space Exploration

In the modern space exploration era, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an essential tool in the search for knowledge. Scientists use AI and ML models to automate spacecraft operations, analyze large quantities of data, and can even save lives. Let’s break down what that looks like:
Robotics
AI plays an increasingly important role in space exploration, with its ability to autonomously navigate around obstacles leading the way. But this is not something recent. Rovers like the Mars Exploration Rover and Curiosity have been doing fully-autonomous navigation drives on the surface of Mars for over ten years.
The rover’s sensors can detect environmental hazards, such as rocks, craters, and other features. Then, its AI analyzes the data to determine the best path forward. This ensures the rover can safely pass by without any risk of collision.
AEGIS, a computer vision-based detection system, similarly runs onboard the Perseverance rover and finds interesting rocks to sample. This is a huge advancement as it paths the way to completely autonomous space exploration rovers.
Satellite Operations
AI is revolutionizing how satellites are operated, providing more efficient, smarter, and faster solutions for managing satellite operations.
SpaceX uses AI-driven algorithms to help its navigation satellites avoid collisions with others in orbit. The algorithms use a combination of data from the satellite’s sensors, including its position and velocity, to identify potentially hazardous maneuvers and take evasive action. The satellite’s onboard computer then takes control and adjusts the satellite’s speed and direction to avoid an imminent collision.
AI can also optimize the process of maneuvering satellites into their correct orbits, reducing the fuel required and the period needed to achieve the desired orbital position.
Data Analysis
AI can help with data analysis in space exploration by providing more accurate and efficient methods of analyzing data from space missions. Machine learning algorithms can assist in identifying patterns in data from satellites, probes, and other space exploration tools to detect anomalies that could signal potential discoveries or risks.
AI can also help identify data trends and provide more detailed insights through predictive analytics and forecasting than traditional data analysis methods.
Planetary Geology (Astrogeology)
Using AI, scientists can now detect and classify geological features on planets and moons, such as craters, volcanoes, and other surface features. This technology can also be used to generate detailed 3D models of planetary surfaces, which can help scientists better understand a planet or moon’s environment and history.
Rocket Landing
SpaceX has been improving and refining how rockets operate. They use AI to monitor and analyze data from the rocket’s sensors and telemetry systems, allowing for better decision-making and more precise control of the rocket’s trajectory and speed. SpaceX also uses AI to automate certain aspects of the rocket landing procedure, such as controlling the engines and landing gear and making sure the rocket is in the optimal position to land.
Star and Galaxy Mapping
Astronomers can now map the universe in unprecedented detail thanks to AI-based algorithms that can detect, classify, and recognize patterns in star and galaxy data. These algorithms allow astronomers to accurately identify stars and galaxies in space and even understand their physical properties (like mass and age). And, by leveraging AI to predict the behavior of stars and galaxies over time, scientists can get invaluable insights that can be used for future mapping and exploration endeavors.
Predictive Maintenance
We’ve seen that AI analyzes large quantities of data to help with satellite operations and rocket landing procedures. Still, it can also use the same data to identify potential areas where preventive maintenance should be conducted.
Machine learning models can predict future failures or performance issues and recommend action plans to reduce the risks. This can drastically reduce maintenance costs and help save countless lives.
Get To Know Other Data Science Students
Bret Marshall
Software Engineer at Growers Edge
Garrick Chu
Contract Data Engineer at Meta
Karen Masterson
Data Analyst at Verizon Digital Media Services
AI in Space Exploration: The Past, Present, and Future
In recent years, AI has become an integral part of space exploration. It has been used to uncover phenomena that humans could not easily detect, such as changes in orbital paths or objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye.
A little while ago, AI was mainly used to analyze data gathered by satellites and other instruments, such as Hubble Space Telescope images. AI algorithms were also used to search for patterns and insights in this data so that researchers could better understand the universe around us.
Today, AI is used for various space exploration applications ranging from autonomous navigation systems on spacecraft to virtual simulations for training astronauts. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory has recently developed an AI-based mission planning system that can autonomously plan a spacecraft mission based on given parameters and constraints. And machine learning algorithms are being used to analyze millions of images gathered from Mars rovers to identify potential water sources or mineral deposits on the planet’s surface.
Looking ahead into the future of space exploration, AI will increasingly be implemented across various future missions in space—from asteroid mining and Mars colonization initiatives to interplanetary travel and beyond.
Past
Here’s what the history of AI in space exploration looks like:
Deep Space 1

Deep Space 1 (DS1) was a NASA technology demonstration spacecraft launched in 1998. Its primary mission was to test 12 advanced, high-risk technologies, including autonomous navigation. The mission was extended twice and concluded in 2001.
Deep Space 1 made history when its flight experiment was controlled by Remote Agent, a feat that had only been seen in science fiction up to that point. That artificial intelligence exceeded all expectations. It could detect, diagnose and fix any problems encountered during the mission. This proved that the software could make decisions to keep the mission running smoothly.
Earth Observing-1
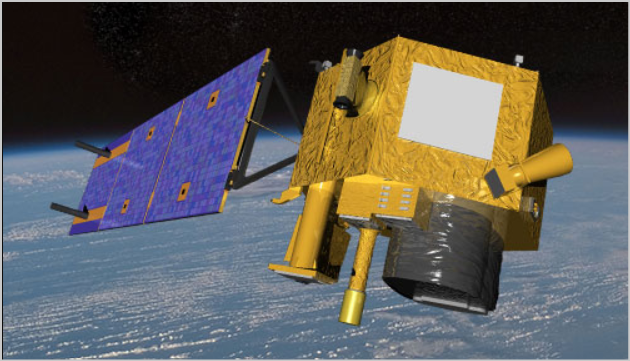
Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) is a satellite imaging mission developed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Launched in November 2000, EO-1 was designed to demonstrate new Earth observation technologies and provide an advanced capability for monitoring land surface dynamics.
The mission utilized an innovative spacecraft design integrated with three high-resolution sensors to create new opportunities for observing the Earth’s environment. The data collected from these sensors is used to study various topics, including ecological processes, natural hazards, land use change, urban planning, and global climate change.
EO-1 was equipped with a revolutionary software program called Autonomous Science Agent. It allowed EO-1 to autonomously detect and respond to events occurring on the planet. This package consists of systems for science data analysis, deliberative planning, and run-time robust execution.
Present
Here’s where AI in space exploration stands today:
James Webb Space Telescope and Morpheus
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or Webb) is a space telescope that was launched in 2021. It is much larger than its predecessor (the Hubble Space Telescope) and has a 21 feet (6.5 meters) primary mirror, making it the largest outer space telescope ever built.
NASA’s scientists rely on AI to analyze the vast amount of data being generated by Webb with the help of Morpheus, a machine learning model. Morpheus will detect and classify galaxies in deep space, helping map the earliest structures in the universe. The AI has been trained on Nvidia GPUs and previously used to help organize images for the Hubble Space Telescope.
Crew Interactive Mobile Companion (CIMON and CIMON-2)

Crew Interactive Mobile Companion (CIMON) is a robotic AI-based assistant created by Airbus, IBM, and the German space agency (DLR) for use in the International Space Station. CIMON is a free-floating spherical device about the size of a medicinal ball that contains voice recognition, facial recognition, object recognition, and natural language processing capabilities. It can help astronauts with tasks like assembling equipment or providing instructions.
AI-Powered Rover “Pragyan” for India’s Second Moon Mission – Chandrayaan-2
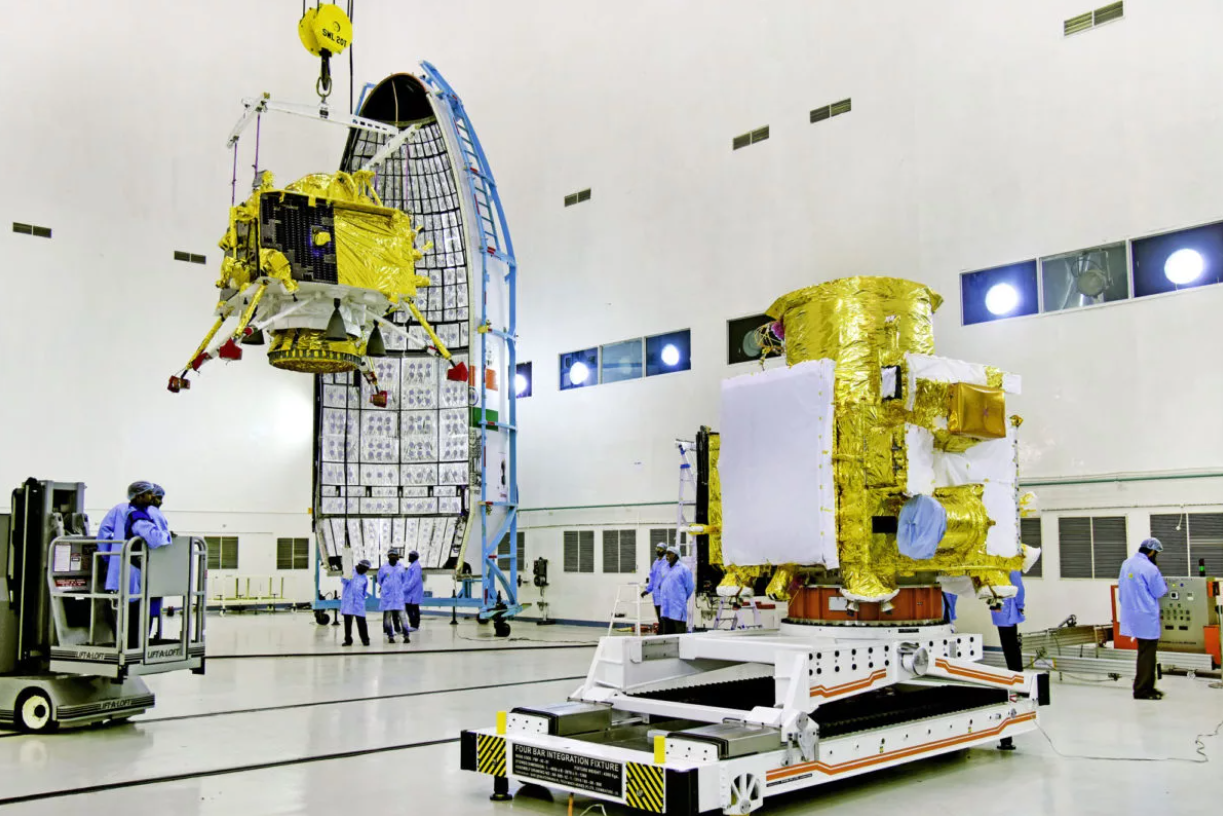

Pragyan is an AI-powered rover that is part of Chandrayaan-2, India’s second moon mission. It will explore the lunar surface and search for water, minerals, and other resources.
The rover has been designed to traverse the lunar surface and perform various scientific experiments. An AI system enables it to navigate autonomously and identify, analyze, and respond to its environment in real-time, much like the 19-year older system tested in the Earth Observing-1 mission.
Kepler Data

Kepler was a space telescope designed to search for Earth-sized planets in the habitable zone of their host stars. Through nine years of data collection, Kepler has made over 2,600 discoveries, including the first validated Earth-size planet in the habitable zone outside our solar system.
The data collected by Kepler will continue to be analyzed by the team of researchers to discover more planets and further guide astrobiology science. And as machine learning techniques become more powerful, we expect scientists to discover even more exoplanets in the near future, all based on existing data.
Future
Artificial Intelligence is opening new possibilities and will soon revolutionize the way we think of space expiration. NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission is scheduled to arrive at the Sun’s outer atmosphere in December 2024.
The probe will be within 4 million miles of the Sun’s surface and can tolerate temperatures as high as 2500℉ (or 1370℃). It is equipped with a magnetometer and an imaging spectrometer that will help us understand how the Sun interacts with other planets in our solar system, thus allowing us to comprehend solar storms, which often interfere with communication technology on earth.
AI is expected to improve our ability to monitor Earth-orbiting observation satellites and spacecraft on long-distance voyages. By combining AI with robotics, we might see astro robots that can explore distant planets and moons by themselves.
FAQs About AI in Space Exploration
We answer your most frequently asked questions:
Does NASA Use AI?
Yes! NASA uses AI in many operations, from analyzing space missions and spacecraft data to monitoring spacecraft’s health, controlling robotic arms and rovers on other planets, and more.
What Are the Disadvantages of Using AI in Space Exploration?
AI can significantly help space exploration, but it does so at a cost, mainly because it’s rather expensive. Moreover, AI is still limited in its capabilities and may not be able to provide the same level of insight as humans do.
How Is Machine Learning Used in Space Exploration?
Machine learning algorithms are used to analyze data gathered from space-based instruments, such as telescopes and satellites, optimize their efficiency, and discover patterns and anomalies.
Since you’re here…
Thinking about a career in data science? Enroll in our Data Science Bootcamp, and we’ll get you hired in 6 months. If you’re just getting started, take a peek at our foundational Data Science Course, and don’t forget to peep our student reviews. The data’s on our side.





