Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Salary, Skills, & Background

In this article
- Is There a Difference Between a Data Analyst and a Data Scientist?
- The Discipline
- The Role
- Education, Skills, and Background
- Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist Skills
- Career Path
- Salary: Data Scientist vs. Data Analyst
- Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Day In the Life
- Becoming a Data Professional: Where to Start
Information is power, and nowhere is this more prescient than in the world of big data. Even seemingly innocuous data can—when collected and analyzed—produce actionable insights for businesses. This is why the fields of data science and data analytics are now experiencing rapid growth, with the number of data science jobs increasing by 650% since 2012, and data analytics jobs looking to increase by another 22% before 2030.
However, the terms “data scientist” and “data analyst” are so often used interchangeably that it can be difficult to parse their differences. And this can be especially confusing if you’re trying to break into the field of big data. That’s why we’ve created this guide. Below, we’ll detail the skills and background needed for each role, in addition to their respective salaries.
Is There a Difference Between a Data Analyst and a Data Scientist?
There is no official standard that dictates when a role should be titled “data scientist” or “data analyst,” so you will likely come across various overlaps and contradictions when browsing the job market. However, many consider the role of a data scientist to involve more coding, deeper analysis of data, and investigations into more abstract questions.
The Discipline
To fully understand the differences between the two fields, let’s have a look at their respective definitions.
What Is Data Analysis?
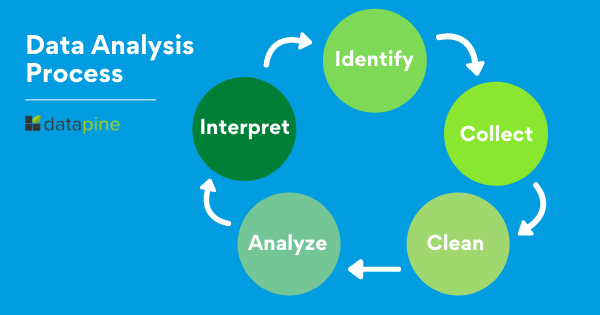
Data analysis refers to the in-depth study of data in order to find patterns that can be translated into useful insights. When structured and queried appropriately, formerly incomprehensible data can become a goldmine of relevant and profitable information that can be used by companies in all kinds of industries.
For example, data analysis can tell a clothes shop what product is most popular at what time and with which demographic—which can then help staff decide what kind of promotions to run. Data analysis can also help social media sites work out what, when, and how to advertise to individual users in order to maximize the number of clicks.
What Is Data Science?
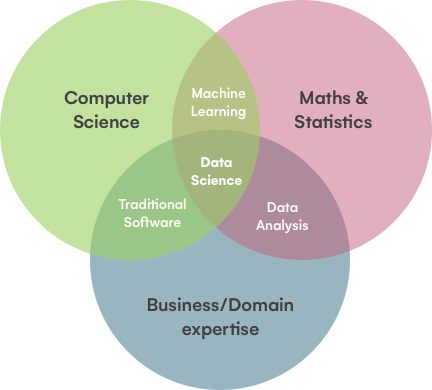
Source: IronHack
Data science shares an ultimate goal with data analysis: finding valuable insights within mountains of complex or seemingly trivial data. Often, rather than carrying out the analysis itself, data science focuses on designing the models and writing the algorithms that will be used during the data analysis process.
While data analysis uses past data to provide insights that can inform future decisions, data science aims to use that data to predict the outcome of future decisions. The developing fields of machine learning and pattern recognition are used to make predictions based on extremely large volumes of past data.
Get To Know Other Data Science Students
Hastings Reeves
Business Intelligence Analyst at Velocity Global
Pizon Shetu
Data Scientist at Whiterock AI
Haotian Wu
Data Scientist at RepTrak
The Role
Now that we’ve covered the outlines and objectives of data analysis and data science, let’s look at how the roles of data analysts and scientists contribute to these goals.
What Does a Data Analyst Do?
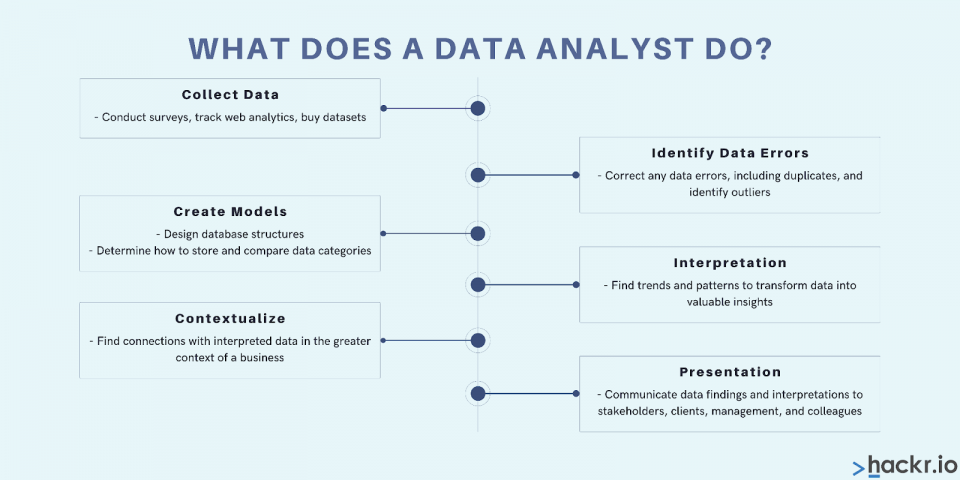
Unsurprisingly, a data analyst analyzes data. This involves collecting data from different sources and putting it through the processes of data wrangling and data mining. These processes structure and glean insights from the data that can then be presented to those who might act on them.
A data analyst is often given questions by stakeholders and decision-makers and asked to find a way to answer them. This means collecting and correlating relevant data and piecing it together to create a bigger picture.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?
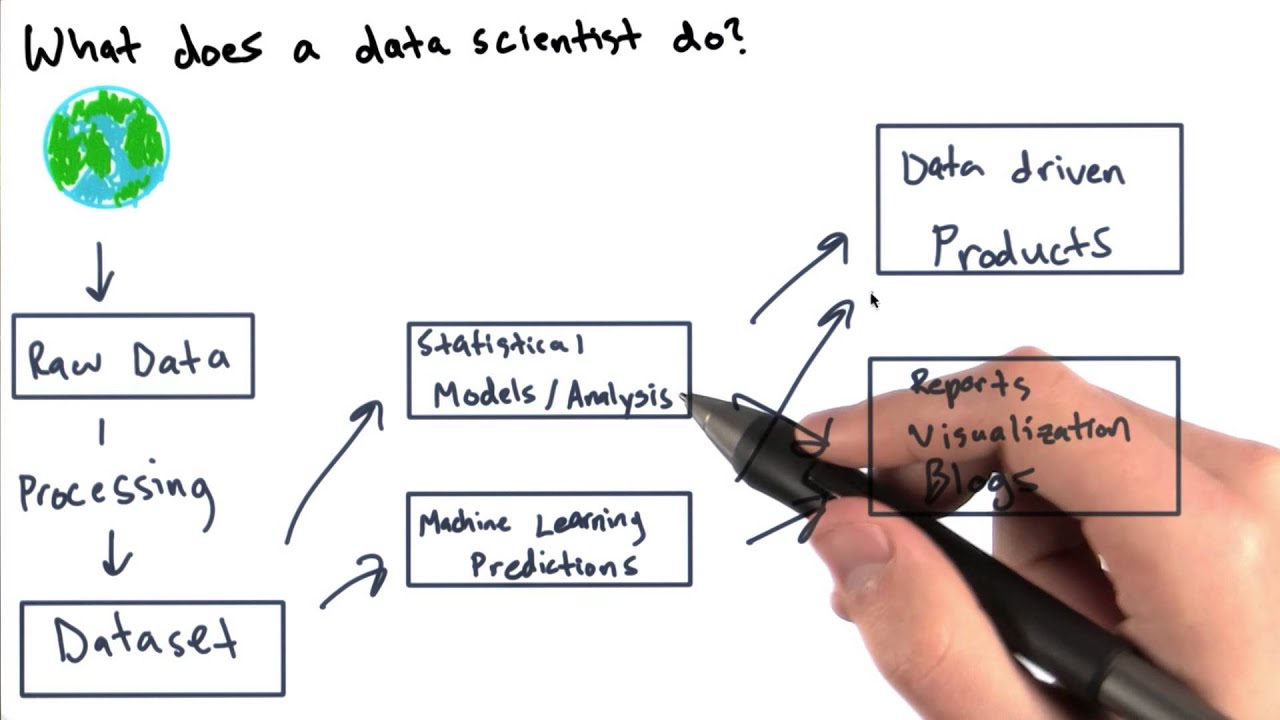
A data scientist can have a few varying roles within a company, some of which are very similar to a data analyst—including collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to gain useful information. However, where a data analyst is likely to have received specific questions to find the answers to, a data scientist might instead analyze the same set of data with the objective of unearthing patterns that could lead to a new line of inquiry. In other words, a data scientist has the job of finding the right questions, as well as the right answers.
Aside from this, a data scientist will design models and write algorithms and software aiming to streamline the data analysis process for both themselves and their data analyst team members. A recent study found that cleaning and structuring data takes up more of a data scientist’s time than any other task, so constant efforts are being made to automate more and more of this process so that more time can be devoted to analysis.
A data scientist is also more involved in the field of machine learning (deep learning) and aims to push the boundaries and discover new ways for this technology to be put to practical use in a business setting. This can include running models that predict possible outcomes of hypothetical situations posed by the data scientist.
Education, Skills, and Background
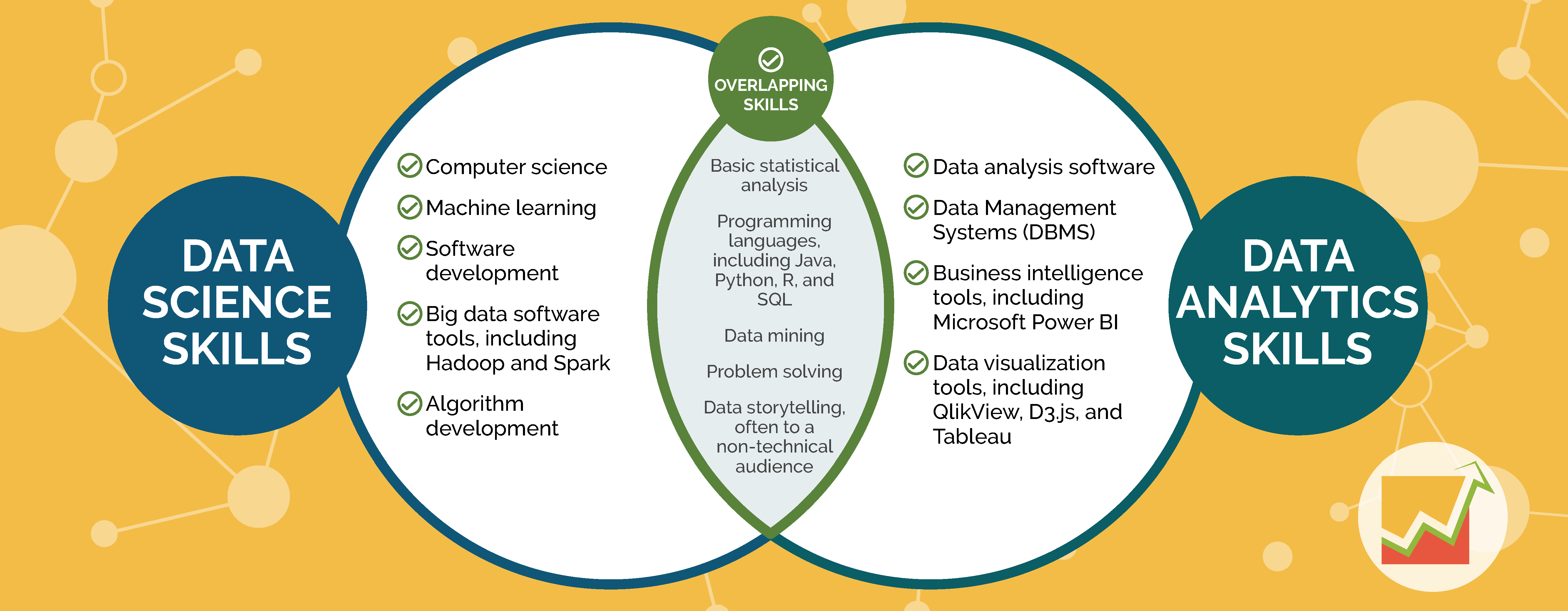
While there are now college courses and online bootcamps designed specifically for these roles, this wasn’t always the case. That’s why you’ll find a lot of senior data scientists and analysts with backgrounds in varying fields.
What Are the Requirements To Become a Data Analyst?
Below, we’ll list some common requirements found in job advertisements for data analyst roles.
- Bachelors or advanced degree related to computer science, statistics, or the company in question.
Or
- Master’s degree or higher related to computer science, statistics, or the company in question.
- Soft skills, including communication, flexibility, organization, and project management.
- Experience and skill in communicating insights derived from data to both technical and non-technical personnel.
- Experience with Microsoft Excel, Tableau, and other industry tools.
- Proficiency in SQL, Python, and/or R as well as applicable libraries/packages.
- The ability to plan and carry out projects with minimal direction.
What Are the Requirements To Become a Data Scientist
Below, we’ll show you the common requirements listed in job postings for data scientists.
- Bachelor’s degree in math, statistics, computer sciences, or related to the employer. (Note that 37% of data scientists have bachelor’s degrees.)
Or
- Master’s or advanced degree or higher in math, statistics, computer sciences, or a field related to the employer. (Similarly, 31% of data scientists have master’s degrees or PhDs.)
- Quantitative and analytical skills.
- Experience with industry tools such as Python, SQL, SAS, and R.
- Excellent soft skills to facilitate effective collaboration between teams and departments.
- Knowledge and interest in economic and industry trends, with keen business acumen.
- Familiarity and experience with data visualization and applicable tools such as Microsoft Excel and Tableau.
- Self-starting, with the ability to work effectively with minimal guidance.
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist Skills
Skills and requirements as listed on job postings can be a bit idealistic and a little vague. Here is a more concrete list of technical skills data analysts and data scientists need to get their jobs done.
What Skills Does a Data Analyst Need To Succeed?
The beginning of a project for a data analyst often comes in the form of desired information or answers to questions posed by stakeholders and higher-ups in the company. The end of a project is the presentation of the acquired insights and answers to these questions. In order to get from point A to point B, the following data analyst skills are required and expected from employers:
- The ability to take questions and requests posed by non-technical employees and determine what kind of information is acquirable and from what kinds of data.
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Python (and its packages,) SQL, R, and SAS in order to collect, wrangle and analyze the relevant data.
- Excellent research skills to obtain a deeper knowledge of the questions posed and answers desired so that data sets can be enriched in order to increase the value of the insights they can provide.
- Proficiency in data visualization tools which will be used to showcase data-derived insights in a format that’s easy to comprehend by people of both technical and non-technical backgrounds.
- Excellent communication skills to ensure that all the valuable information obtained is clearly and accurately conveyed to the right people so that action can be taken.
What Skills Does a Data Scientist Need To Succeed?
As well as finding answers, a data scientist often also has the job of posing questions or determining valuable questions to pose. They are often tasked with the “unknowns,” such as using predictive models to project potential outcomes of business decisions or future industry trends. They also design and write algorithms, models, and software that can help to automate the process of cleaning and wrangling data.
Most employers will expect you to have the following data science skills:
- Experience in data analysis and its processes (data discovery, data wrangling, data mining). Knowing how data works and what kinds of insights might be hiding within it is essential for a data scientist to pursue new lines of inquiry.
- Deep knowledge of machine learning, artificial intelligence, natural language processing (NLP,) statistical models, and other related fields in order to tackle the task of projecting the potential outcomes of various situations.
- Fluency in the programming language Python and other data analysis tools for designing new models and writing new software that can help organize, structure, and clean data with less manual work.
- Excellent soft skills in order to facilitate smooth collaboration between varying teams and departments. This is useful for collecting data from different places, deepening one’s understanding of the topic being analyzed, and communicating results.
Career Path
Nobody becomes a senior data analyst or data scientist overnight—once their education is complete, the average graduate starts off in a junior role and then works their way up.
What Is a Typical Career Path For a Data Analyst?
When it comes to data analysis, building a foundation of knowledge and experience in handling, manipulating, and wrangling data is crucial. Many current senior data analysts have bachelor’s degrees or master’s degrees in related fields. However, as demand increases, more and more people are taking specific data analysis courses at colleges and online. This includes attending online bootcamps as a substitute for a college degree.
For most data analysts, their first role will be as a junior in a larger data analysis team, where they will learn the basics of the job in a practical setting and build up a lot of experience in data wrangling. After a couple of years, a data analyst’s role will expand to include more responsibility and chances to lead and help shape projects. At the most senior level, data analysts become team leaders and take charge of deciding and allocating projects.
What Is a Typical Career Path For a Data Scientist?
A data scientist must make a similar journey to a data analyst. However, in order to be able to delve as deep into data as they do, data scientists also have to build up a strong foundation and familiarity with data. Traditionally, data scientists often come from mathematical backgrounds with PHDs in statistics, computer sciences, and economics. Nowadays, there are college programs and online bootcamps dedicated to data science, and this is how the next generation is being taught.
Before diving into the depths of machine learning and mapping out predictions, a junior data scientist will likely land a role with an emphasis on data wrangling. The process of readying data for analysis is so varied from case to case that it’s a lot easier to learn through hands-on experience. Once familiar with the practicalities of data analysis, a data scientist can branch out into algorithm and software writing, and deepen their knowledge of machine learning and its applications. A more senior data scientist might go down the path of team lead or management roles, allocating projects and working closely with stakeholders and decision-makers. Alternatively, they may spend their seniority tackling the most complex and valuable questions with their expert knowledge in machine learning and pattern recognition.
Related Read: 14 Data Science Careers to Consider [Skills, Salary, Role]
Salary: Data Scientist vs. Data Analyst
In professional fields such as data science and data analytics, advanced experience and advanced skills can raise your salary through the roof. Anonymously reported annual salaries for data analysts on Indeed reach as high as $147,000, and for data scientists, as high as $207,539.
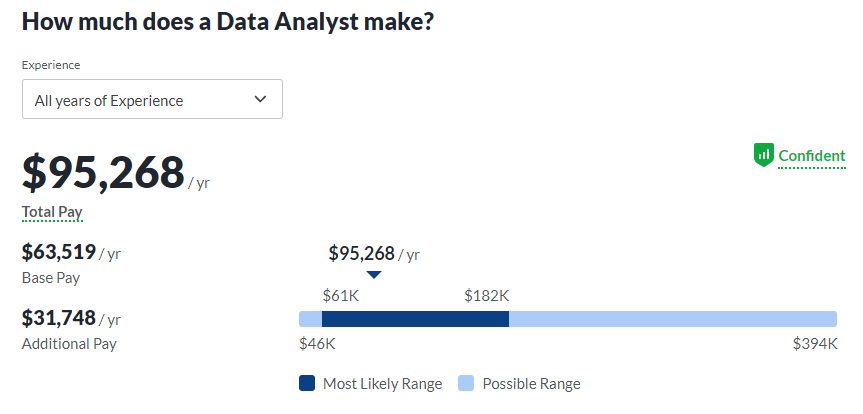
What Does a Data Analyst Make?
Glassdoor and Indeed report similar average salaries for data analysts in the US at $68,950 and $69,692 respectively.
Glassdoor reports an average additional pay of $25,921, which comes in the form of various benefits, including stock sharing.
On Indeed, Washington, DC is reported as the highest paying city for data analysts.
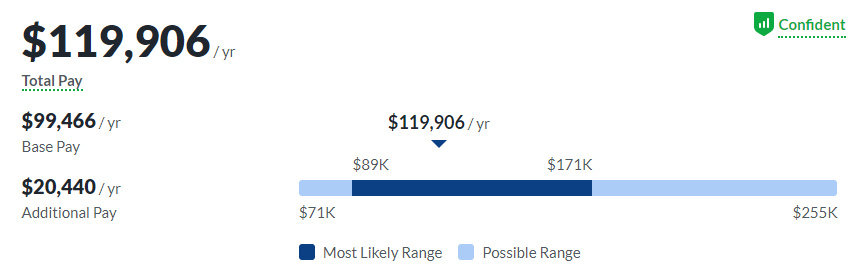
What Does a Data Scientist Make?
For data scientist roles, Glassdoor and Indeed report almost identical average salaries of $101,936 and $102,139.
Reported salaries on Indeed show New York as the highest paying city for data scientists, and Glassdoor reports an additional $18,182 a year in additional compensation, which includes benefits and stock shares.
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Day In the Life
You now know the objectives data analysts and data scientists are aiming for, the skills required to achieve them, and the compensation they receive. However, you might be wondering—what does the daily schedule look like for people in these roles? How do their day-to-day tasks build towards the completion of a project? Let’s have a look!
What Does an Average Day Look Like for a Data Analyst?
- Stand-ups
Communication is a highly important aspect of a data analyst’s daily activities. A good example of communication in action is the daily stand-up, a short and to-the-point meeting typically held each morning between the members of a team. Each person reports what they did the previous today, what they plan to do today, and any problems they’re facing.
- 1-to1s
Another common meeting is the 1-to-1. This often refers to meetings with a team lead or manager, or any third parties involved in the current project.
- Jira (or other sprint-planning platforms)
Data analysis teams often make use of platforms like Jira to plan out one or two-week-long work cycles called ‘sprints.’ This helps individuals keep track of their own tasks as well as those of other team members and even other teams.
- Data diving
Data analysts will likely spend time every day working with the data they are currently analyzing. This can involve cleaning, wrangling, and mining the data, as well as creating and maintaining dashboards and reports.
- Code review
Before changes or updates are officially made, data analysts create ‘pull requests’ on platforms like Github. This publishes the proposed code for other team members to review, approve, or suggest changes to.
What Does an Average Day Look Like for a Data Scientist?
Here are some common tasks you’ll typically see in a day in the life of a data scientist.
- Stand-ups
These morning meetings are very common throughout the tech industry, and they are a typical part of any data scientist’s daily schedule.
- 1-to-1s
Individual meetings with team leads, managers, and clients are also very common. These meetings help keep management up to date with the progression of a project, find out about problems quickly, and manage the well-being of the team.
- Handling data/writing code
At the beginning of a project, a large amount of a data scientist’s time will be spent researching, collecting, and cleaning data, which is often a collaborative task. Further into a project, the main task will change to writing algorithms and code that can return answers to questions the data scientist wants to ask. This work is often done individually.
- Code review
All roles that involve writing and committing code will also involve reviewing code and having one’s code reviewed.
Becoming a Data Professional: Where to Start
There are multiple pathways into the fields of data analytics and data science. Below, we’ll present you with a look at a few.
How To Become a Data Analyst
- Choose a college program in the following areas: computer science, economics, mathematics, engineering, or data analysis.
- Take the self-taught route by building your knowledge on your own schedule, often using free and community-created resources. This free-form approach allows for the focus to be allocated wherever the individual sees fit.
- Enroll in an online data analytics bootcamp, which is a comprehensive course designed to guide students from their first introduction to data analytics all the way to their first job applications.
How To Become a Data Scientist
- Start a bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, or Ph.D. in a related field such as statistics, mathematics, computer science, data mining, engineering, or data science.
- Develop your knowledge individually using various resources, while continuing to work in your current field. This option is great for the motivated individual and can allow for advanced niche and specific knowledge to develop very quickly.
- Study with an online data science bootcamp. These courses combine the structure and guidance of college courses with the flexibility of self-study. They are designed to take you from beginner status all the way to being job-ready
Since you’re here…
Curious about a career in data science? Experiment with our free data science learning path, or join our Data Science Bootcamp, where you’ll only pay tuition after getting a job in the field. We’re confident because our courses work – check out our student success stories to get inspired.






